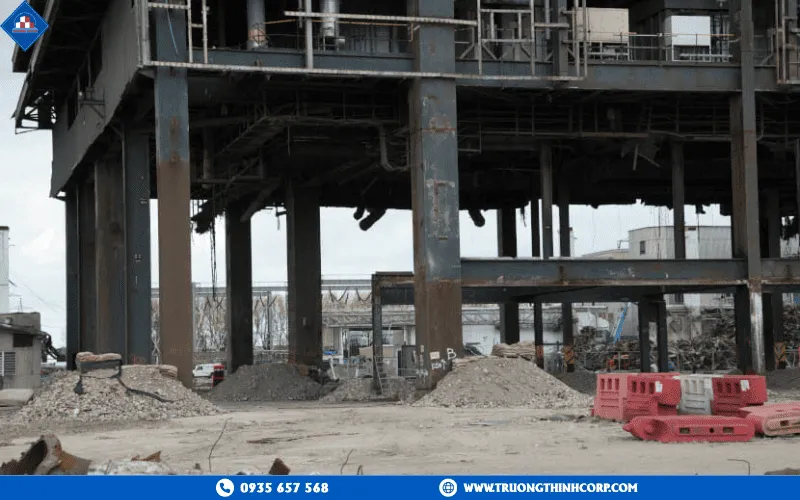
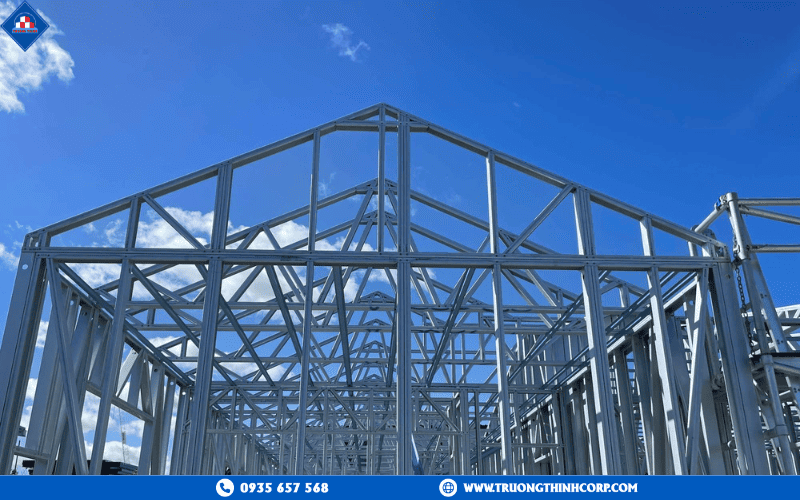
Key Advantages and Applications of Steel Structures in Construction

In the context of rapid urbanization and industrialization, the demand for buildings with high load-bearing capacity, quick construction timelines, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability has become increasingly urgent. Among the many available materials, steel structures in construction have emerged as a modern, sustainable, and efficient solution that effectively balances technical performance, aesthetic value, and economic benefits.
1. What is a steel structure?
Before analyzing advantages, disadvantages, or the erection process, it is essential to understand what steel structures are, how they differ from reinforced concrete, and the principles of load resistance and types of steel commonly used. This foundation enables investors to select the right materials and construction methods for each project type.

1.1 Definition and comparison with reinforced concrete
A steel structure refers to a load-bearing framework composed of steel components such as columns, beams, braces, and frames, connected through welding or high-strength bolts. Compared to reinforced concrete, steel structures in construction are 40–60% lighter, provide superior tensile and compressive strength, and can be easily dismantled and reused, making them an optimal choice for projects that require flexibility, mobility, or future expansion.
1.2 Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB) – A major milestone in construction
One of the most common forms of steel structures today is the Pre-Engineered Building (PEB). All components are designed and fabricated in a factory, then assembled on-site based on precise technical drawings. At Truong Thinh Corp, production takes place within a 25,000 m² closed facility equipped with CNC laser cutting machines, 3-in-1 automatic welding systems, and Sa2.5 shot blasting technology, enabling a monthly capacity of 1,200 tons of steel.
1.3 Load resistance and ductility of steel
Steel can withstand heavy loads without permanent deformation, ensuring structural safety under strong winds or seismic activity. Thanks to its ductility, steel can absorb and dissipate energy, reducing the risk of sudden collapse.
1.4 Common steel grades used in construction
|
Steel grade |
Standard | Key features | Common applications |
| SS400 | JIS G3101 (Japan) | Easy to weld, medium strength | Beams, factory frames |
| A36 | ASTM (USA) | High strength, easy to fabricate | Bridges, industrial frames |
| Q345 | GB/T (China) | High load capacity, durable in harsh environments | High-rise buildings, overpasses |
2. Advantages and disadvantages of using steel structures
Compared to traditional reinforced concrete, steel structures in construction provide remarkable benefits in terms of load-bearing capacity, lightweight design, faster construction speed, and greater architectural flexibility. However, they also present certain limitations, including susceptibility to corrosion, reduced strength at high temperatures, and relatively higher initial investment costs. Therefore, businesses should carefully evaluate both short- and long-term economic efficiency when selecting structural materials.

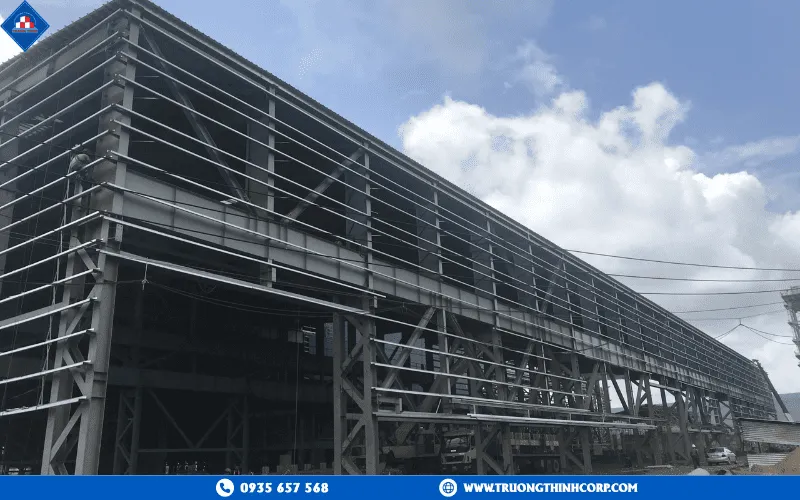
2.1 Advantages
- Superior load-bearing capacity: Steel possesses excellent tensile, compressive, and bending strength, enabling large-span designs (20–50 m) with minimal intermediate columns—ideal for factories, warehouses, and industrial facilities requiring open spaces.
- Lightweight and reduced foundation load: Steel components weigh 40–60% less than concrete, reducing foundation size, saving materials, and lowering substructure costs. This improves overall stability on weak soils and allows for future expansion.
- Fast, flexible, and precise construction: Since steel members are pre-fabricated in factories, on-site erection is quick and accurate without the curing delay of concrete. Construction time is often reduced by 30–50% compared to traditional methods.
- Architectural flexibility: Steel’s versatility allows architects and engineers to design creative, complex structures while maintaining safety and durability.
- Eco-friendly and recyclable: Steel is 100% recyclable, meeting the criteria for green and sustainable construction. It aligns with global efforts to reduce CO₂ emissions and supports green building certifications such as LEED and LOTUS.
- High durability and low maintenance: When coated and maintained properly, steel structures can last over 50 years, requiring far less maintenance than concrete, which is prone to cracking and water infiltration.
2.2 Disadvantages
- Corrosion in harsh environments: In humid, coastal, or chemical environments, steel surfaces may oxidize, leading to rust. Protective coatings such as anti-corrosion paint, hot-dip galvanization, or epoxy coatings are required to extend material life.
- Reduced strength at high temperatures: At 500–600°C, steel loses its load-bearing capacity and may deform under fire conditions. To mitigate this, structures should be protected with fireproof coatings, insulation layers, or automatic sprinkler systems.
- Higher initial investment: Although steel costs more upfront and fluctuates with market prices, the overall life-cycle cost is often lower due to faster construction, reduced labor, and minimal maintenance.
- High technical requirements: Erection demands skilled labor and specialized lifting equipment. Without precise supervision, connection misalignment can compromise safety.
2.3 Economic optimization
To assess economic efficiency, one must consider Life-Cycle Cost (LCC)—including fabrication, maintenance, and reuse. Studies show steel structures can be 10–20% more cost-effective than reinforced concrete due to:
- Shorter construction periods enabling early operation and revenue.
- Reduced maintenance thanks to corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Longer lifespan and reusability during renovations or expansions.
Comparison Table: Steel Structure vs. Reinforced Concrete
| Criteria | Steel structure | Reinforced concrete |
| Load-Bearing capacity | Very high (tension & compression) | Good compression, weak tension |
| Structural weight | 40–60% lighter | Heavy, higher foundation load |
| Construction time | Fast (pre-fabricated) | Slow (requires curing) |
| Dimensional accuracy | High (factory-made) | Depends on site conditions |
| Maintenance cost | Low (if protected) | High (prone to degradation) |
| Average lifespan | 50–100 years | 30–50 years |
| Reusability | Easy to dismantle/recycle | Not reusable |
Thus, steel structures offer greater long-term value, especially for industrial factories, logistics centers, warehouses, and pre-engineered buildings, where construction speed and operational efficiency are top priorities.
3. Common types of steel structures
After understanding their benefits and risks, it is crucial to recognize the different types of steel structures to choose the most suitable system for each project.
3.1 Beams, Columns, Bracings, and Connections
Every steel frame system includes:
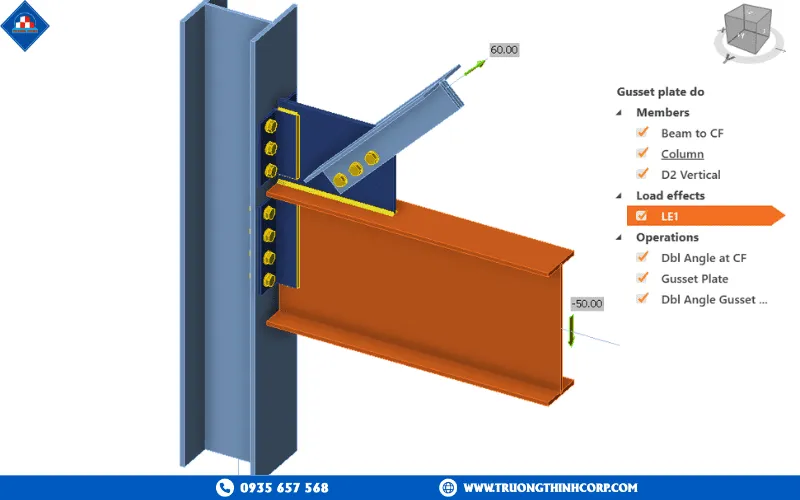
- Beams: Horizontal members resisting bending, often with H or I sections.
- Columns: Vertical members carrying axial loads.
- Bracings: Provide lateral stability and wind resistance.
- Connections: High-strength bolts and JIS-standard welds—executed by Truong Thinh’s Japan-certified welders to ensure international quality.
3.2 Classification by Structural Form
- Frame Structures: Common in factories and logistics centers.
- Truss Structures: Ideal for large-span buildings like warehouses, bridges, and canopies.
- Arch Structures: Used in stadiums and large-span roofs.
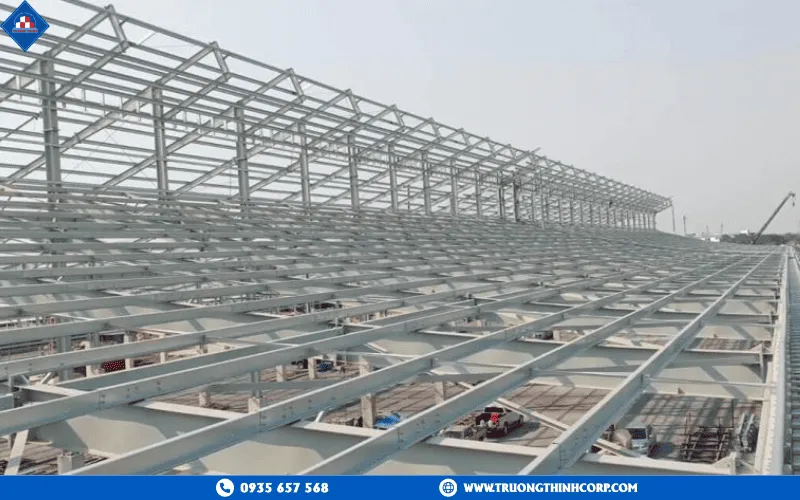

Depending on usage and site conditions, Truong Thinh Corp provides structural solutions that optimize cost, load performance, and durability.
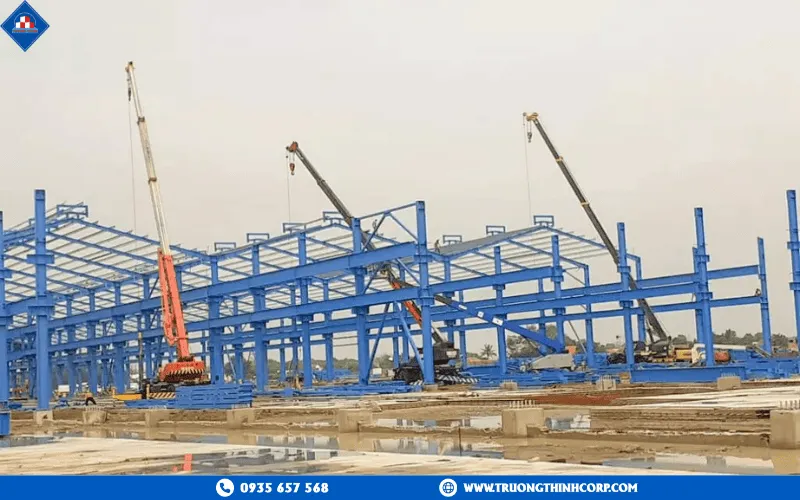
4. Standard steel structure erection process
A quality steel project depends not only on materials but also on precise execution and strict quality control across all phases: engineering design, fabrication & erection, and quality management.
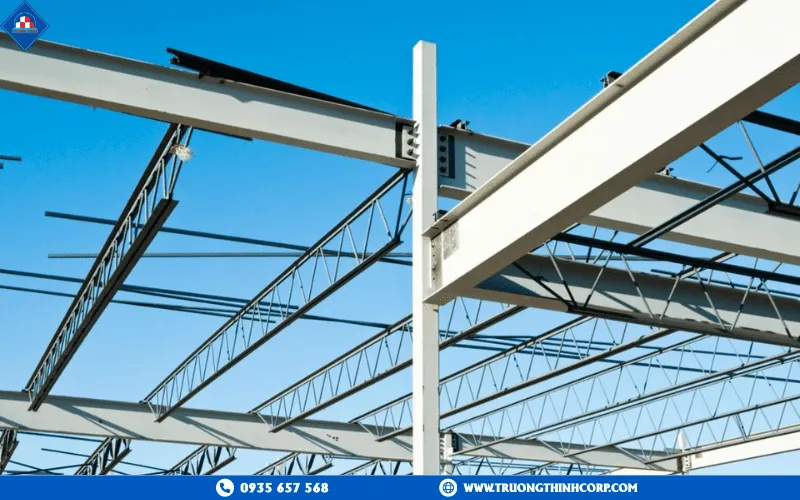

4.1 Construction process
The design phase forms the foundation of the project. Truong Thinh engineers use specialized software such as Tekla Structures, Revit, and SAP2000 to simulate loads, analyze stresses, and optimize frameworks. After approval, all components are fabricated in Truong Thinh’s mechanical factory—laser cut by CNC machines, welded with 3-in-1 Gantry automatic systems, shot-blasted to Sa2.5, and coated with a three-layer epoxy system for corrosion protection. Erection is carried out using the modular assembly method, ensuring precision and shortened schedules. Integrated workflow from design to installation enables tight progress control and absolute on-site safety.
4.2 Quality control
Quality control (QC) is prioritized throughout construction. Every weld, bolt, and joint is checked with laser alignment equipment for dimensional accuracy. All inspection standards comply with ISO 9001:2015, guaranteeing top-tier quality. Each project includes a comprehensive documentation package—site logs, as-built drawings, and material inspection reports—for transparency and long-term maintenance.
4.3 Project management
To ensure seamless coordination, Truong Thinh Corp operates under the EPC (Engineering – Procurement – Construction) model, taking full responsibility from design to completion. The company also applies Tekla BIMsight for real-time progress tracking and resource allocation, ensuring on-time, on-quality, and on-budget delivery.
5. Applications of steel structures
Due to their high strength, fast installation, and design flexibility, steel structures are widely applied in industrial, high-rise, and infrastructure projects.

5.1 Industrial plants and warehouses
Steel structures are ideal for industrial facilities requiring large spans and unobstructed interiors. Unlike concrete, steel frames can achieve clear spans up to 100 meters, maximizing usable floor area and facilitating machinery layout and logistics operations. Prefabrication ensures rapid erection, minimizing production downtime and enabling early operations—critical for ROI optimization.
5.2 High-rise buildings and bridges
The use of steel in high-rise and transportation infrastructure is increasing in Vietnam. Lightweight yet strong, steel reduces foundation loads—especially valuable in dense urban or soft-soil areas. Composite Steel Structures (steel + concrete) combine the advantages of both materials, enhancing flexural, compressive, and vibration resistance for skyscrapers and bridges.
5.3 Design and construction standards in Vietnam
Truong Thinh Corp strictly adheres to Vietnamese standards such as:
- TCVN 5575:2012 – Design of steel structures (strength, stability, economy)
- TCVN 170:2007 – Hot-rolled steel products for construction
For international projects, AISC 360 and ASTM A36 standards are applied, meeting export requirements to the U.S., Cambodia, Singapore, and beyond. By integrating multiple international standards, Truong Thinh ensures its steel structures meet the highest levels of durability, safety, and technical excellence, reflecting the company’s global competence and engineering credibility.
Steel structures represent not only a fast, durable, and flexible construction solution but also a significant advancement in bringing Vietnam’s construction industry closer to international standards. With full EPC capability, modern production facilities, and a highly skilled team of engineers, Truong Thinh Corp is dedicated to providing comprehensive steel structure solutions that cover every stage of the process, from design consulting and fabrication to on-site erection, serving partners across various industries. For project collaboration or inquiries, please contact Truong Thinh Corp for more information.