Classification of Steel Structures for Modern Construction
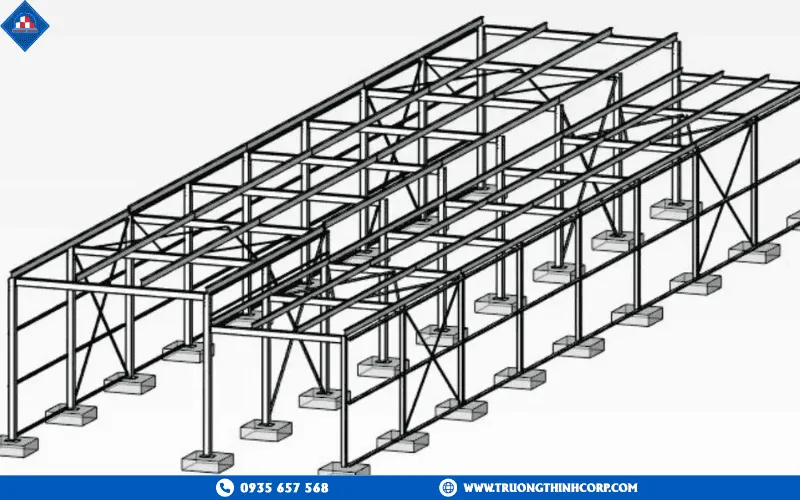
In the era of rapid industrialization and urbanization, steel structures have become a fundamental element of modern construction, serving a wide range of projects including factories, warehouses, shopping centers, bridges, and energy infrastructure. With outstanding strength, durability, design flexibility, and recyclability, structural steel is considered the backbone of 21st-century construction. The true value of steel structures lies not only in the material itself but also in the way they are categorized, selected, and applied to suit each project. This article offers an overview of the main types of steel structures, their strengths and limitations, real-world applications, and the international material standards commonly used across the industry.
1. Classification of steel structures by shape
Depending on load-bearing characteristics and functional requirements, steel structures can be categorized into several shape-based groups. Each type offers unique advantages to meet specific structural and architectural demands.

1.1. Frame structures
Steel frames consist of columns and beams connected by bolts or welds, forming the primary load-bearing system of a building.
- Features: Excellent performance under vertical, wind, and lateral loads.
- Applications: Industrial buildings, high-rise towers, shopping centers, and logistics warehouses.
- Advantages: Easy to expand, modular assembly and disassembly, suitable for large-span buildings without internal columns.
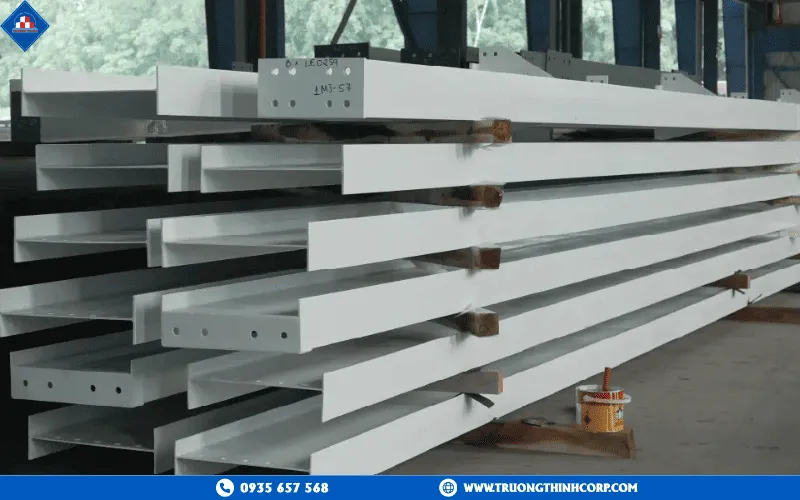
Example: At Truong Thinh Steel Structure Plant (Binh Duong), H-Beam frames are fabricated using an automated 3-in-1 welding line and CNC plasma cutting system. All welds undergo ultrasonic testing (UT) to ensure durability and precision within ±1 mm tolerance.
1.2. Truss structures
Formed from interconnected steel members arranged in triangular patterns, trusses efficiently distribute loads.
- Advantages: Optimized material use, lightweight yet highly load-resistant.
- Applications: Industrial roofs, stadiums, airport terminals, and large-span warehouses.
- Disadvantages: Complex fabrication and assembly, requiring high accuracy.
1.3. Arch structures
Arched or parabolic configurations transfer loads primarily through compression along the curve.
- Advantages: Even load distribution, spacious appearance, and high architectural aesthetics.
- Applications: Steel roofs, exhibition halls, and long-span bridges.
Example: Several commercial projects by Truong Thinh, such as Co.op Mart Ha Tien and Dong Phu, utilize composite steel arch roofs that are both lightweight and architecturally distinctive.
1.4. Space frame structures
Space frames consist of three-dimensional interlocking steel members that distribute loads in multiple directions.
- Advantages: Capable of spanning up to 100 meters, efficient load dispersion, lightweight and durable.
- Applications: Sports arenas, exhibition halls, and large-span factories.
- Technical note: Requires complex dynamic analysis and high fabrication precision.
1.5. Cable structures
These structures use high-tensile steel cables to support the entire system, creating lightweight and elegant forms.
- Applications: Suspension bridges, cable-stayed bridges, canopies, and stadium roofs.
- Advantages: Extremely lightweight, capable of very long spans, suitable for landmark projects.
- Disadvantages: Requires regular maintenance and high-strength steel such as ASTM A572 or equivalent.
2. Classification by construction method
The construction method directly affects project duration, cost, and structural performance. Below are common types based on fabrication and assembly techniques.
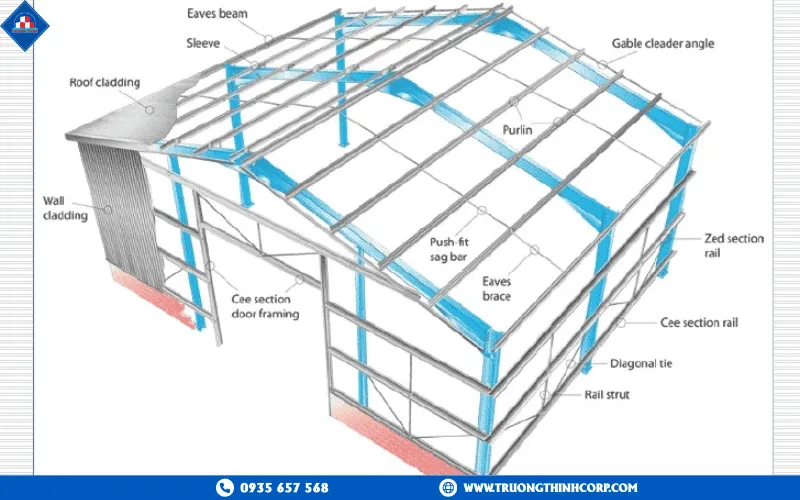
2.1. Composite steel–concrete structures
This system combines the tensile strength of steel with the compressive strength of concrete.
- Monolithic type: Columns and beams are encased in concrete to act as a unified load-bearing system.
- Bonded type: Steel is anchored or bonded within concrete, suitable for bridges and service floors.
- Advantages: Enhanced fire resistance, reduced vibration, and greater stiffness.
- Applications: Overpasses, high-rise buildings, foundations, and bridge piers.
2.2. Light-gauge steel structures
Made from galvanized steel with small cross-sections, these systems are standardized for efficiency.
- Advantages: Lightweight, fast installation, and cost-effective.
- Applications: Residential housing, temporary buildings, mini-warehouses, and agricultural facilities.
- Note: Suitable for light loads, not recommended for heavy industrial projects.
2.3. Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB)
A modern construction solution where all structural components—columns, rafters, purlins, and beams—are pre-fabricated in the factory and assembled on-site.
Advantages:
- Construction speed 2–3 times faster than reinforced concrete.
- Strict quality control under ISO-standard environments.
- Optimized material and weight efficiency.
Applications: Factories, warehouses, supermarkets, logistics centers, and exhibition halls.
Example: Truong Thinh Corp’s steel structure plant in Binh Duong has a capacity of 1,200 tons per month, featuring 12-m CNC plasma cutting lines, 18-m portal welding machines, and beam straighteners rated at 24.2 kW, enabling flexible production from light to heavy industrial structures under ISO 9001:2015 certification.
3. Classification by steel member type
Steel members are the fundamental components of every structure. Understanding their properties ensures efficient design and construction.
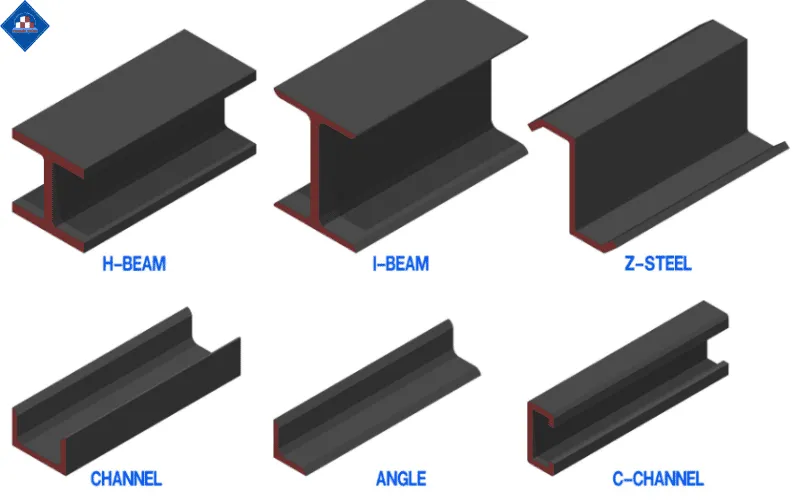
| Steel Member Type | Characteristics and Applications |
| I-Beam | I-shaped cross-section, excellent bending resistance, used for floor beams and primary frames |
| L-Angle | Two perpendicular flanges, used as bracing or secondary framing |
| C-Channel | C-shaped, lightweight, suitable for purlins and lintels |
| T-Beam | Cut from I-Beam, used as intermediate floor beams |
| Pipe (Round/Square/Rectangular) | High torsional resistance and aesthetic appeal |
| Hollow Section (Box Steel) | Reduces weight, suitable for space frames and architectural structures |
| H-Beam | Wide flange and web, strong under compression and bending, ideal for load-bearing columns |
At Truong Thinh Corp, commonly used materials include SS400 and Q235-A, both offering excellent weldability and load-bearing capacity for main frames, roof trusses, and secondary beams.
4. Applications of steel structures
Steel structures today extend far beyond industrial factories to commercial, infrastructure, and public facilities. With high load capacity, fast construction, and design flexibility, they meet technical, economic, and aesthetic requirements for large-scale developments.
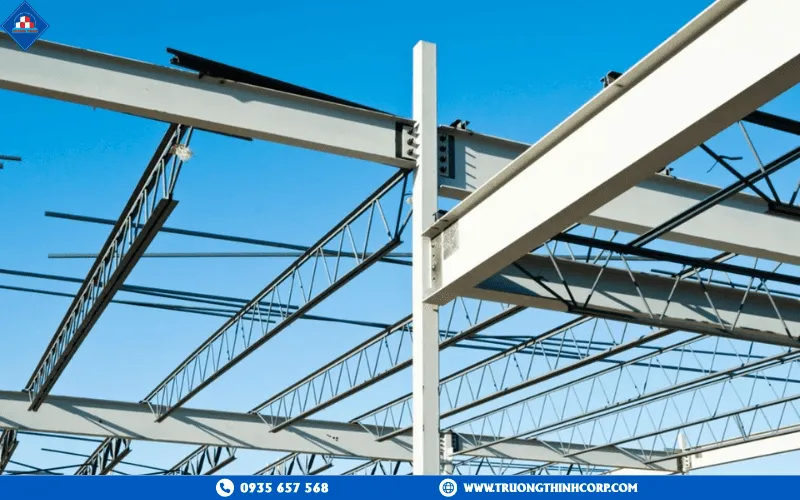

4.1. Industrial and commercial applications
In industrial and commercial construction, steel structures enable flexible production spaces, reduced construction time, and easy expansion. With high load resistance and modular connections, factories, warehouses, malls, and manufacturing plants can be built quickly while maintaining safety and longevity.
Typical solutions include Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB) for warehouses and logistics centers, industrial plants with cranes or conveyor systems requiring high precision, and large-span facilities such as exhibition halls or sports arenas that demand open interiors without columns.
Real-world examples include Truong Thinh Corp’s projects such as Dabaco Binh Phuoc Factory, Vam Co Port Warehouse (Dong Nai), and Co.op Mart Ha Tien and Thap Muoi, all constructed using automated welded steel frames on CNC production lines for speed, accuracy, and industrial aesthetics.
4.2. Infrastructure and transportation applications
Beyond industry, steel structures are increasingly used in infrastructure and transportation. Their lightweight nature, high strength, and long-span capability make them ideal for bridges, stations, toll plazas, and elevated structures.
In bridge design, beam or cable-stayed steel systems reduce foundation loads and shorten construction time compared with concrete. Stations and toll facilities often use composite frames or space trusses to reduce roof weight and achieve modern architectural appeal.
In key industrial projects, Truong Thinh has successfully applied 20-ton overhead cranes, hybrid space frames, and 18-m welded girders, showcasing Vietnam’s capability in advanced steel structure engineering for national infrastructure and major FDI developments.
5. International standards for structural steel selection
Selecting the right structural steel is critical for safety and quality. Global standards define not only steel grades and mechanical properties but also design and load-calculation methods. Two main aspects are steel grade standards and cross-section design standards.
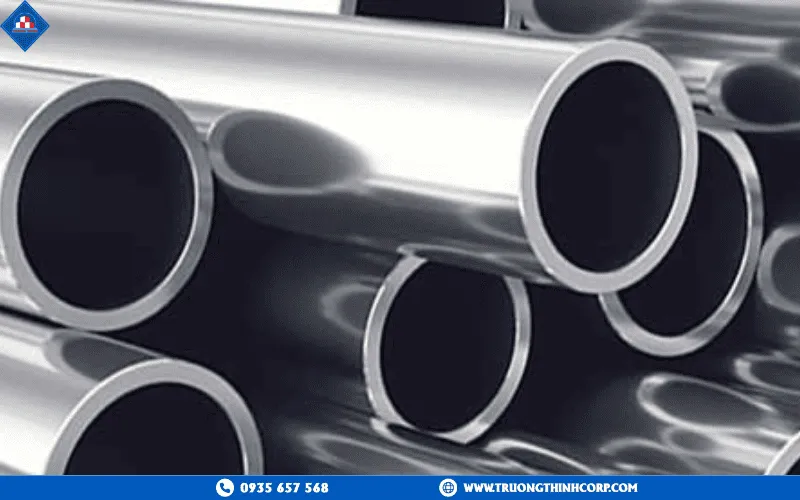

5.1. Common steel grades and standards
Structural steel today is produced under several international systems:
ASTM (USA):
- A36: Medium-carbon steel, easy to weld, tensile strength 400–550 MPa.
- A572: High-strength steel used for bridges and long-span frames.
JIS (Japan):
- SS400: Equivalent to ASTM A36, high ductility and easy fabrication.
- SM490: Alloy steel for heavy-duty infrastructure.
TCVN (Vietnam): TCVN 1651-85, TCVN 1977: Define mechanical properties and testing methods.
EN (Europe): S235, S275, S355: Carbon steel grades with increasing strength.
In Vietnam, reputable manufacturers such as Truong Thinh Corp use SS400 and Q235-A, which are imported and quality-tested under ISO 9001:2015 standards before fabrication.
5.2. Cross-section design and standards
Common standard sections include:
- H, I shapes: Excellent in bending and compression, used for columns and main beams.
- C, Z shapes: Used for purlins and bracing, optimizing material use.
- Box sections: Offer aesthetic appeal for architectural designs.
Design calculations often refer to AISC (American Institute of Steel Construction) or Eurocode 3, which specify load, stress, and moment analysis methods.
Structural steel is more than just a building material; it represents a complete solution for modern construction. The appropriate choice of structural type, material grade, connection method, and surface protection directly determines the durability and service life of each project. Companies with comprehensive capabilities in design, fabrication, and installation, such as Truong Thinh Corp, demonstrate that steel structures represent the future of construction, where efficiency, quality, and sustainability are seamlessly integrated in every detail.
👉 To learn more or discuss your upcoming steel structure project, contact Truong Thinh Corp today.





