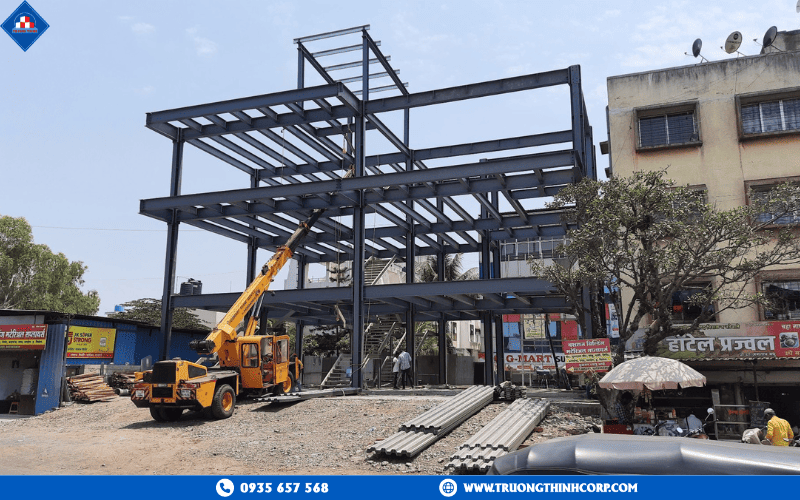
Steel Structures in Residential Construction

Steel structures in residential construction are becoming an increasingly popular choice for townhouses, villas, homestays, and modern houses thanks to their fast erection speed, open-space design capability, and high-quality control throughout the design and fabrication stages. This article provides a concise overview of key concepts, main components, advantages and limitations, design requirements, technical solutions, and contractor selection guidelines to help homeowners make informed decisions when considering a steel frame solution for their residential projects.
1. What is a steel structure in residential construction?
A steel structure in residential construction refers to the primary load-bearing frame of a house, fabricated from structural steel sections such as H-beams, I-beams, box columns, built-up sections, or pre-formed steel plates. Instead of conventional on-site concrete casting, the structural members are pre-manufactured, surface-treated, and assembled using high-strength bolts or welded joints according to detailed shop drawings.
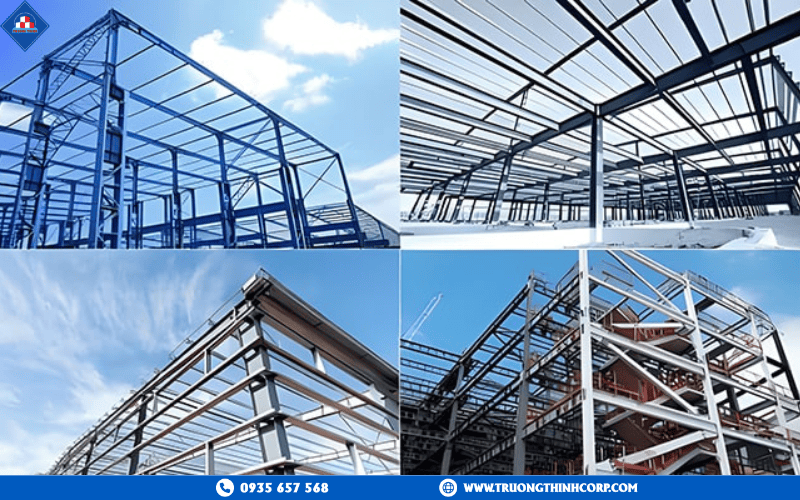
1.1 What are the main components of a steel frame system?
- Columns & Beams: Typically made from H-shaped, I-shaped, or box sections (built-up or rolled). Columns carry vertical loads, while beams transfer horizontal loads. Connections are commonly executed with base plates and high-strength bolts or welds in accordance with relevant structural standards.
- Floor System: Composite deck floors (steel deck combined with lightweight concrete) or full steel floors are used to provide rigidity while reducing overall structural weight.
- Bracing & Torsion Restraints: Horizontal and diagonal bracing members, along with anti-torsion systems, ensure stability under wind and dynamic loads.
- Connections & Bolts: High-strength bolts and detailed connection drawings must be strictly controlled to maintain structural safety and precision during assembly.
- Surface Protection: Protective coatings such as epoxy paint, intumescent fireproof paint, or anti-corrosion coatings are applied to extend the lifespan of the steel components.
1.2 Which types of residential buildings should use steel structures?
Steel structures are ideal for a wide range of residential projects, including:
- Narrow Urban Houses (Townhouses): Reduce construction time, dust, and noise during installation.
- Villas & Modern Homes: Create open spaces and contemporary architectural aesthetics.
- Vertical Extensions & Renovations: Lessen foundation loads and allow for lightweight, flexible construction.
- Resort Homes / Homestays: Enable modular expansion, easy assembly, and functional adaptability.
1.3 What to prepare before building a steel frame house
Before starting construction, it is essential to clearly define the functional goals, number of floors, and requirements for sound insulation, thermal insulation, and fire resistance, along with your budget and acceptance standards. Selecting a turnkey contractor that manages design, fabrication, and erection with an in-house CNC manufacturing facility helps minimize risks and ensures quality control throughout the process.
Below are the key documents and technical requirements that should be prepared before signing the contract to ensure safety and efficiency when using steel structures in residential construction:
- Preliminary design documents: Floor plans, sectional drawings, and proposed structural schemes.
- Technical requirements: Specifications for acoustic performance, thermal insulation, and fire protection standards.
- Budget & schedule: Cost comparison between steel and reinforced concrete structures.
- Contractor selection criteria: Workshop capacity, fabrication capability, and QA/QC management system.
2. Advantages and disadvantages of steel structures compared to reinforced concrete
In modern residential construction, the competition between steel framing and reinforced concrete is no longer just a matter of material choice. It represents a difference in design philosophy and construction efficiency. Each structural system offers unique strengths, but steel frames are increasingly demonstrating their superiority through lightweight performance, high precision, and architectural adaptability. However, to achieve optimal results, investors must understand both the advantages and limitations of steel framing in order to choose the most suitable solution for their residential projects.

2.1 Why is steel frame construction faster?
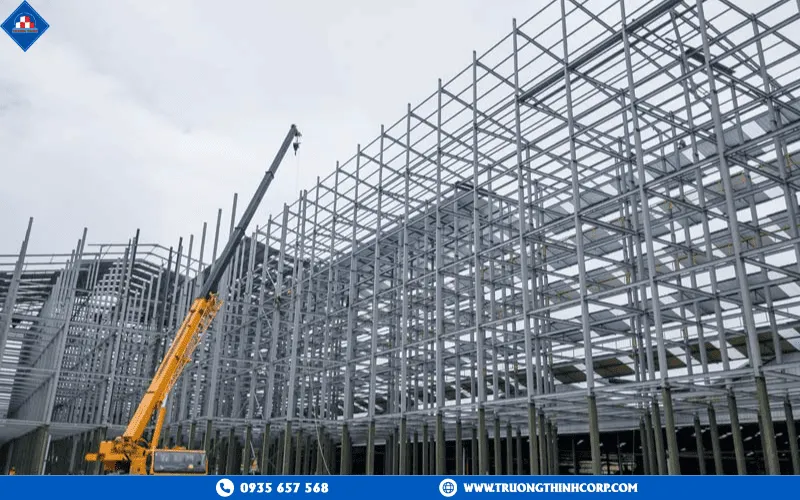
Unlike traditional reinforced concrete structures, which require multiple stages of formwork installation, pouring, curing, and stripping, steel-framed houses are prefabricated in the factory and only assembled on site. At Truong Thinh Corp, all steel components are produced on modern CNC production lines—from cutting, welding, and drilling to finishing with precision paint coating—maintaining a tolerance of less than 1mm. This streamlined process reduces construction time by 40–50%, while minimizing quality risks caused by weather conditions. On-site, components are bolted together using high-strength bolts, with no wet concrete, no curing time, and no complex field operations required.
2.2 Are steel frames durable and safe?
The durability of a steel frame depends not only on the material itself but also on design standards and quality control procedures. Mechanically, steel provides tensile and compressive strength that is many times greater than concrete. It does not crack, shrink, or settle over time. When properly designed and protected, steel structures can last from 50 to 70 years, which is equivalent to or even longer than reinforced concrete. This longevity, combined with consistent manufacturing precision, ensures long-term safety and stability for residential applications. However, limitations in sound and thermal insulation can be addressed through proper design solutions and the use of advanced insulation materials.
One of the most common concerns about steel-frame houses is their acoustic and thermal performance. Compared to concrete, steel conducts heat and sound more efficiently, potentially making interiors hotter or noisier if not properly treated. However, thanks to modern construction materials, these issues are effectively addressed using advanced insulation solutions:
- External walls: Typically composed of multi-layer lightweight panels, featuring rock wool or fiberglass insulation for soundproofing and Cemboard or moisture-resistant gypsum boards for the outer layer. This system minimizes sound transmission while maintaining indoor temperature stability.
- Roof system: Treated with heat-reflective coatings or PU/PIR insulated panels, capable of reducing radiant heat by up to 70%, keeping interiors cool even during hot seasons.
- Floor system: Composite deck floors or multi-layer acoustic materials help absorb vibrations and reduce impact noise between levels, providing a solid and quiet living experience comparable to traditional concrete houses.
3 What are the key design criteria for residential steel structures?
Design is the most critical foundation in the construction of a residential steel-frame building. A well-engineered design not only ensures structural safety but also achieves aesthetic harmony, functional efficiency, and optimal investment performance. To ensure long-term stability and durability, structural engineers must carefully calculate loads, spans, deflection limits, vibrations, and connection details, as well as anti-vibration and stiffness control. Close coordination with the architectural and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) teams is essential to achieve a fully integrated and high-performance building system.
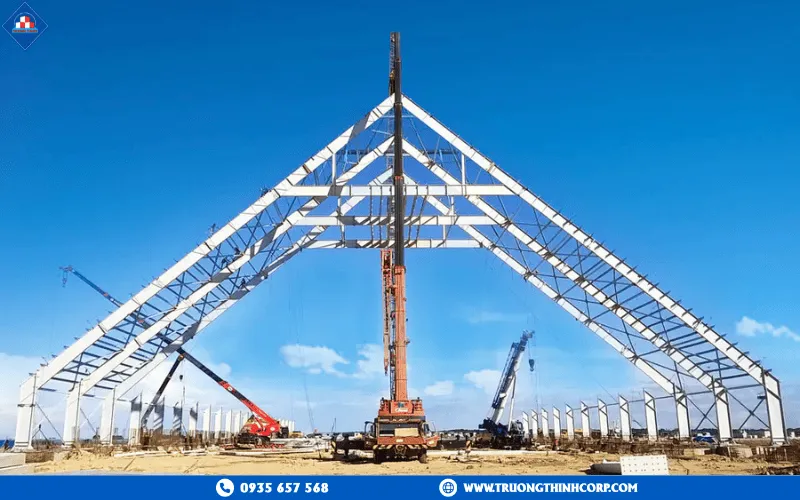

3.1 Span and deflection control for living rooms and large open spaces
The span, which is the distance between two supporting points of a beam or column, is a key factor in determining the sense of openness in a house. In modern residential projects such as living rooms, grand foyers, or double-height spaces, achieving wide spans while maintaining controlled deflection is a critical engineering requirement.
According to design standards, the allowable deflection ratio for residential steel frames typically ranges from L/250 to L/300, where L represents the span length. This ensures overall structural stability and minimizes vibrations under dynamic loads such as foot traffic or furniture movement.
3.2 Fire protection solutions for steel frames in residential buildings
In high-temperature environments, especially during a fire, steel begins to lose its structural strength when it reaches around 500°C. Therefore, designing and implementing fire protection systems is an essential part of modern residential steel structure projects.
At Truong Thinh Corp, engineers incorporate fire resistance measures right from the design stage, calculating the required fire-resistance duration for each structural element and selecting appropriate protection methods:
- Intumescent fireproof coating: When exposed to heat, the coating expands to form a 5–10mm thick insulating layer, slowing heat transfer to the steel core.
- Fire-resistant cladding: Columns and beams are wrapped with fire-rated gypsum boards, fireproof panels, or lightweight concrete blocks, extending fire resistance up to 90 minutes.
- Fire compartments and airtight detailing: Proper compartmentalization and airtight connections prevent fire spread between floors and reduce the risk of localized collapse.
By integrating these comprehensive solutions, Truong Thinh’s projects not only comply with TCVN 2622:1995 (Vietnam Fire Safety Standard) but also exceed conventional residential safety requirements, providing maximum protection for both occupants and property in the event of a fire.
4. Construction and erection process of steel frame houses
The standard workflow includes the following stages: Survey → 3D Design → Factory Fabrication → Painting & Inspection → Transportation → On-site Erection → MEP Installation → Final Inspection & Handover. Each stage must undergo QA/QC procedures to control fabrication tolerances, weld quality, and on-site safety during assembly.
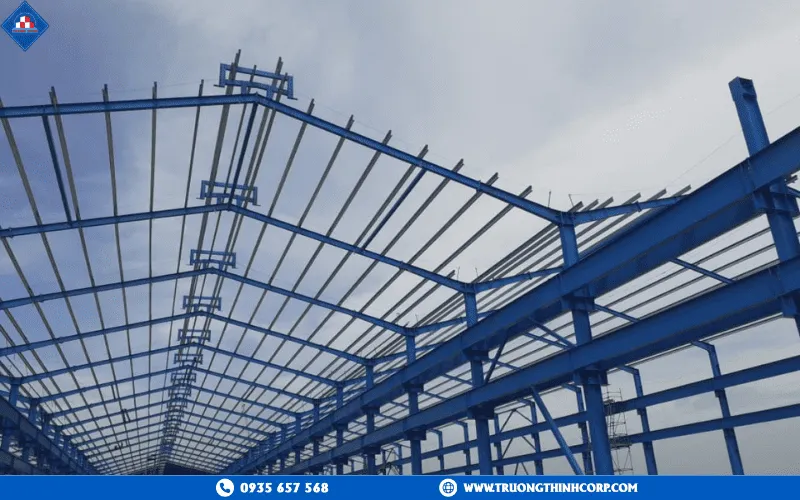

4.1 Precision control and safety during lifting & erection
The erection process requires total station or laser measurement, axis alignment, and strict verification against 3D shop drawings. With proper execution, assembly tolerances can be maintained within ±3 mm. All bolts must be tightened using torque-controlled tools, and the construction team must hold valid welding and rigging certificates. Strict compliance with lifting and safety protocols is mandatory to prevent accidents and ensure structural accuracy.
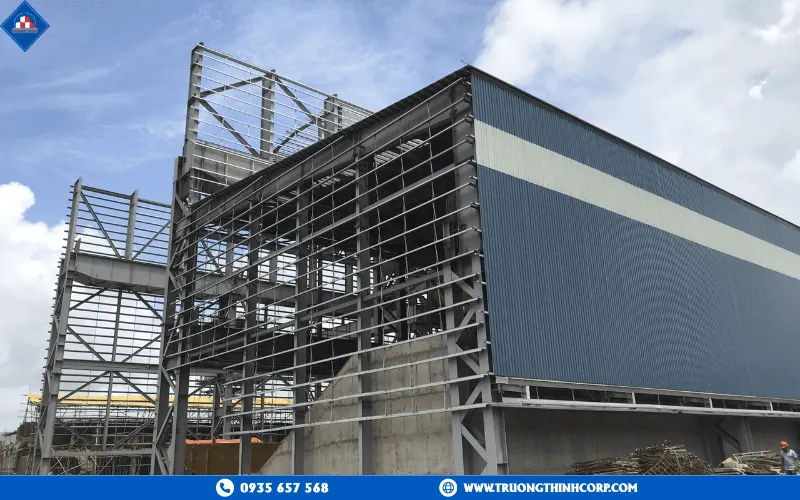
4.2 Building enclosure and interior finishing with steel frames
Once the main frame is erected, cladding and interior finishing proceed quickly using lightweight materials such as EPS panels, tempered glass, aluminum louvers, gypsum ceilings, and composite deck floors. The MEP system (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) is neatly integrated within the technical spaces between beams, enabling efficient installation and easy maintenance.
4.3 Typical construction timeline
A 2–3 story steel-frame house (150–250 m²) can typically be completed within 60–100 days, including:
- 10–15 days for design and 3D modeling
- 15–25 days for fabrication and coating at the factory
- 30–60 days for on-site erection and finishing
This schedule is 30–40% faster than conventional reinforced concrete construction, while maintaining high precision and consistent quality.
5. How to choose the right steel frame contractor to avoid construction risks
Selecting a reliable steel structure contractor requires a thorough evaluation of their design capability (Tekla, SAP2000, Revit), fabrication capacity (CNC workshop, monthly production tonnage), QA/QC system (ISO 9001 certification), portfolio of completed projects, and contract commitments (warranty, timeline, and penalty clauses).

5.1 Key interview questions before signing a contract
Before finalizing any agreement, investors should interview and assess the contractor’s actual capabilities. Asking the right questions helps verify technical competence and clarify their commitment to schedule, safety, and quality. Below are essential question groups to consider:
Design and shop drawing capability:
- Do you use 3D modeling software such as Tekla Structures, SAP2000, or Revit for clash detection and detailed shop drawing generation?
- Are your design documents independently reviewed, and do they include clear material take-offs?
Fabrication capacity and production line:
- Can your factory handle multiple projects simultaneously?
- Are cutting, welding, drilling, and painting machines regularly inspected and calibrated?
QA/QC (Quality Control) procedures:
- Do you apply ISO 9001:2015 standards in your quality management system?
- How do you manage incoming material inspection and component acceptance testing at the factory?
Fire safety and occupational safety:
- Are steel members coated with fire-resistant or anti-corrosion paint?
- Do your erection crews hold certified welding and safety licenses (local or international)?
These questions may seem simple, but they help filter out unqualified contractors and identify truly professional, transparent partners. At Truong Thinh Corp, all QA/QC procedures, inspection reports, and competency certifications are fully transparent, ensuring clients’ absolute confidence throughout the project.
5.2 Essential contract terms to finalize before construction
A clear and detailed contract serves as both a technical and legal safeguard to prevent potential risks during construction. Regardless of project size, the following terms must be explicitly defined in any residential steel structure contract:
- Materials and technical standards: Specify steel types (H, I, built-up box sections), protective coatings, fireproof paint, and relevant standards (TCVN, JIS, ASTM).
- Tolerances and accuracy: Define acceptable deviation limits for each member, erection position, and bolt torque.
- Construction schedule: Clearly outline milestones for design, fabrication, erection, and finishing phases, along with penalties for delays.
- Acceptance, handover & warranty: Detail inspection procedures, warranty period, maintenance conditions, and technical support.
- Penalties and safety commitments: Include penalties for delays, liability in case of incidents, and project insurance requirements.
At Truong Thinh Corp, all contracts are standardized under the ISO management system, ensuring transparency, precision, and full legal compliance. The company also provides long-term warranties for steel frames, along with periodic maintenance and inspection of coatings, bolts, and joints to preserve both durability and aesthetics over time. Steel structures have become an ideal solution for modern housing, offering fast construction, flexible spaces, and strict quality control. When designed correctly, precisely fabricated, and executed by a qualified contractor, steel frames can achieve strength and safety equal to or even greater than reinforced concrete. Thorough preparation of design and technical documents, combined with proper insulation, fireproofing, and a transparent contract, is the key to ensuring a durable and successful residential steel structure project.
To receive detailed consultation and tailored solutions for your home, contact Truong Thinh Corp today for expert support from our experienced engineering team.